前言
在我们写界面的过程中,常常需要改变控件的形状等,如果使用代码控制就太麻烦了,所以一直使用的shape,刚好在博客上看到了一篇很详细的博客,就拿过来当做笔记了。免得需要的时候找不到了,顺便分享给大家。
shape文件的使用
新建shape文件
首先在res/drawable文件夹下,新建一个文件,命名为:shape_radius.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<corners android:radius="20dip"/>
<solid android:color="#ff00ff"/>
</shape>
在控件中使用
在定义好shape文件后,下一步就是将其添加到控件中,添加到控件中,一般是使用设置background属性,将其为控件背景,下面,我们将其设置为MainActivity对应的布局中(activity_main.xml),将其设为TextView的背景,看显示出来 是什么样子的。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.harvic.tryshape.MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="50dip"
android:text="@string/hello_world"
android:background="@drawable/shape_radius"/>
</RelativeLayout>
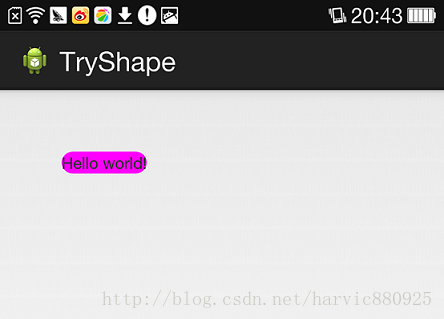
基本属性详解
1、Corners用来指定圆角
<corners //定义圆角
android:radius="dimension" //全部的圆角半径
android:topLeftRadius="dimension" //左上角的圆角半径
android:topRightRadius="dimension" //右上角的圆角半径
android:bottomLeftRadius="dimension" //左下角的圆角半径
android:bottomRightRadius="dimension" /> //右下角的圆角半径
2、solid用来指定内部填充色
<solid android:color="color" />
3、gradient
gradient用以定义渐变色,可以定义两色渐变和三色渐变,及渐变样式,它的属性有下面几个:
<gradient
android:type=["linear" | "radial" | "sweep"] //共有3中渐变类型,线性渐变(默认)/放射渐变/扫描式渐变
android:angle="integer" //渐变角度,必须为45的倍数,0为从左到右,90为从上到下
android:centerX="float" //渐变中心X的相当位置,范围为0~1
android:centerY="float" //渐变中心Y的相当位置,范围为0~1
android:startColor="color" //渐变开始点的颜色
android:centerColor="color" //渐变中间点的颜色,在开始与结束点之间
android:endColor="color" //渐变结束点的颜色
android:gradientRadius="float" //渐变的半径,只有当渐变类型为radial时才能使用
android:useLevel=["true" | "false"] /> //使用LevelListDrawable时就要设置为true。设为false时才有渐变效果
4、stroke 描边属性,可以定义描边的宽度,颜色,虚实线等
<stroke
android:width="dimension" //描边的宽度
android:color="color" //描边的颜色
// 以下两个属性设置虚线
android:dashWidth="dimension" //虚线的宽度,值为0时是实线
android:dashGap="dimension" /> //虚线的间隔
5、size和padding
这两个基本上不怎么用,因为他们所具有的功能,控件本身也能实现。
size:是用来定义图形的大小的。
<size
android:width="dimension"
android:height="dimension" />
padding用来定义内部边距
<padding
android:left="dimension"
android:top="dimension"
android:right="dimension"
android:bottom="dimension" />
Shape的属性(rectangle、oval、line、ring)
上面我们讲了Shape的子标签的的作用,但Shape本身还没讲,Shape自已是可以定义当前Shape的形状的,比如上面的矩形,还有椭圆形,线形和环形;这些都是通过Shape标签的 shape属性来定义的,Shape标签总共有下面几个属性,我们一个个讲:
android:shape=["rectangle" | "oval" | "line" | "ring"] shape的形状,默认为矩形,可以设置为矩形(rectangle)、椭圆形(oval)、线性形状(line)、环形(ring) 下面的属性只有在android:shape="ring时可用: android:innerRadius 尺寸,内环的半径。 android:innerRadiusRatio 浮点型,以环的宽度比率来表示内环的半径, android:thickness 尺寸,环的厚度 android:thicknessRatio 浮点型,以环的宽度比率来表示环的厚度,例如,如果android:thicknessRatio="2", android:useLevel boolean值,如果当做是LevelListDrawable使用时值为true,否则为false.
可见,只有第一个shape是可用的,其它五个都是shape等于ring时所特有的。
注意,无论这里shape取什么形状,他的子标签都是可用的,但有时并不会有效果,比如在shape为椭圆时,那corners标签就不会有效果,很显然的道理。下面一个个看看各个形状都是怎么样的;
本文转载自:启舰的博客